Today I would like to give a quick brief insight into the structure of a 3D printer. Whether you are interested in the topic and you are planning to buy a 3D printer or not, everyone has heard about it in recent years.
To give you an overview of how a 3D printer works, I would like to use the following pictures to explain the individual components.
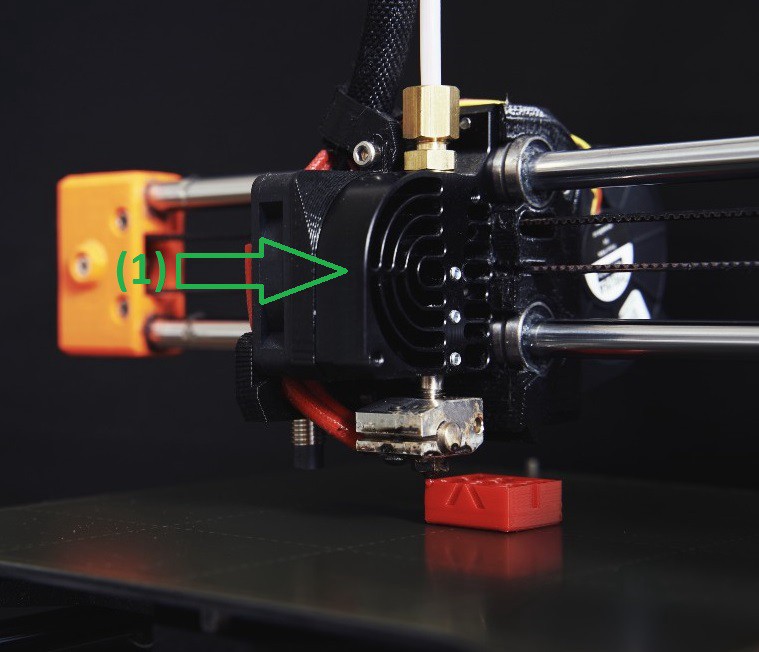
(1) Extruder
The extruder, along with the hot end, is the heart of any printer. The extruder is responsible for pushing the filament forward little by little in order to be able to print exactly the required amount of material.
(2) Hot End
The Hot End is the heat source to melt the filament. In simple terms, it is just a metal block that is heated and has an integrated temperature sensor. In the optimum case, the hot end maintains a constant pressure temperature with the help of the temperature sensor.
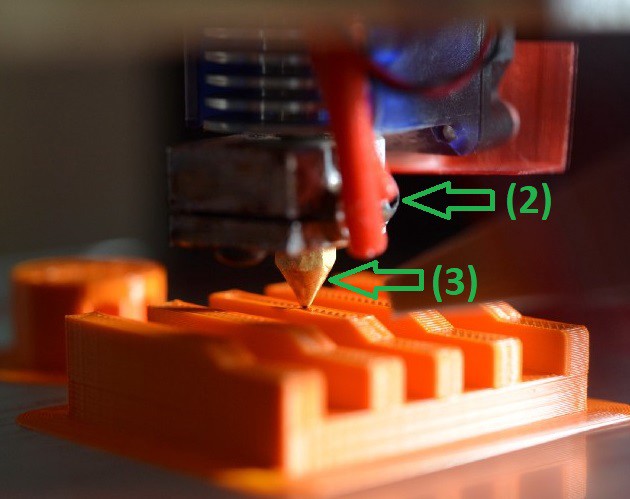
(3) Nozzle
The material heated by the hot end is pressed through the nozzle to produce a narrow, uniform filament for printing. Nozzles can be replaced and usually have a diameter between 0.3 and 0.6 mm in the hobby sector. The most commonly used nozzle has a diameter of 0.4 mm.
(4) Printbed / Heatbed
The print bed is a smooth surface on which the 3D model is printed layer by layer. In most cases, this can be heated so that there is better adhesion of the print material to the surface.
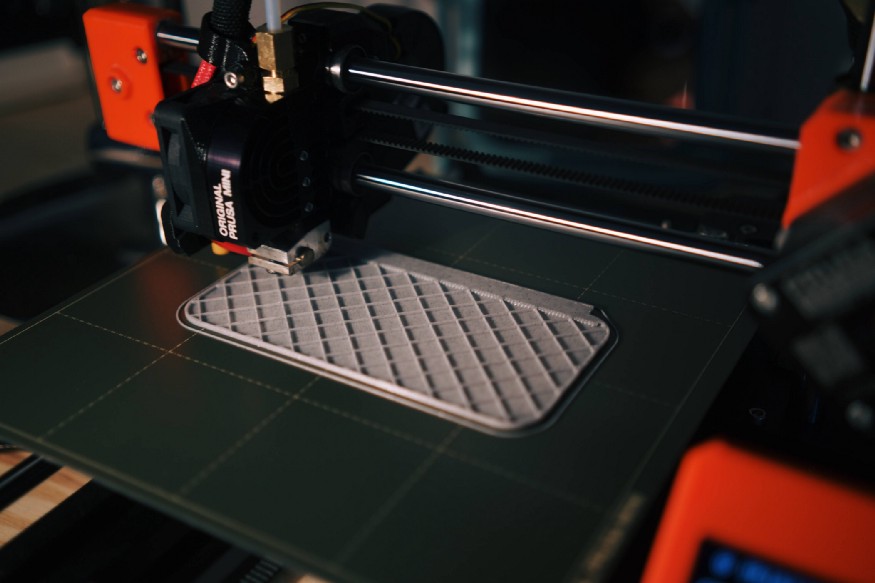

In most cases, the print bed moves on rails along the Y-axis to make Y-movements possible.
(5) Filiament
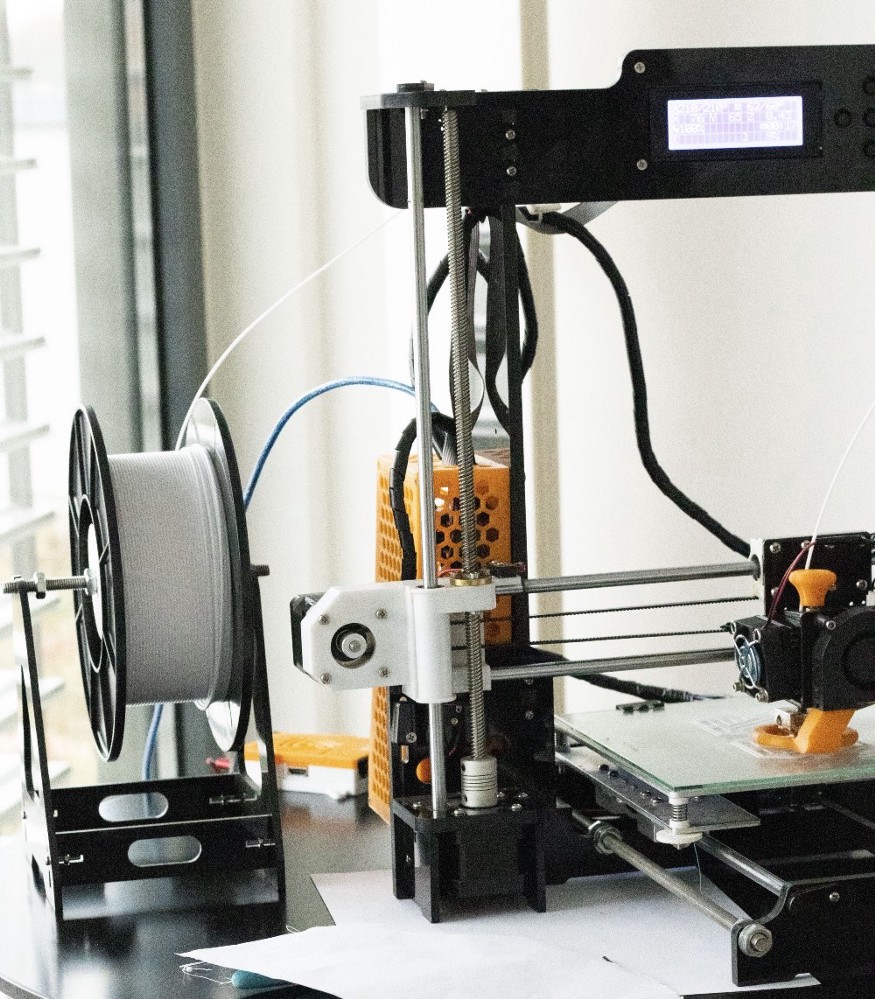
The filiament is the material (usually plastic) from which the 3D model is printed. Common filiaments are PLA, ABS or PETG. Each filiament has its own properties and advantages and disadvantages. It is important to note that there are different thicknesses of filiament, for different extruders. The most common thickness is a diameter of 1.75mm.
I hope I was able to give you an understanding of how the components of a 3D printer works.
If you like my work, feel free to check out my other articles on similar topics.

Schreibe einen Kommentar